Master the 12 English Tenses in just minutes! Learn with simple examples, clear rules & real-life usage — perfect for students, teachers, and English learners of all levels.
Understanding the 12 English tenses is the foundation of mastering grammar and fluent communication. Whether you’re writing, speaking, or preparing for exams like IELTS or TOEFL, tenses help you express time, action, and meaning accurately. In this complete guide, we’ll break down every tense — from Present Simple to Future Perfect Continuous — with clear examples, easy rules, and quick tips so you can finally learn them once and for all.
Table of Contents
1. Present Indefinite Tense
You use the present indefinite tense (or simple present tense) in the following situations:
- To describe habitual actions or routines:
Actions that occur regularly, usually every day, week, or month.- I go to the gym every morning.
- She drinks coffee at 7 AM.
- To state general truths or facts:
Facts that are always true or universally accepted.- Water boils at 100°C.
- The Earth orbits the Sun.
- To express unchanging situations or conditions:
Things that are constant or permanent.- He works in a hospital.
- They live in London.
- To talk about scheduled events (often for public transportation, timetables, or events that are planned):
- The train leaves at 10 AM.
- The meeting starts at 3 PM.
- To give instructions or directions:
- First, mix the ingredients together.
- Turn left at the traffic lights.
- For future events in fixed or scheduled contexts (like timetables or programs):
- The concert begins at 8 PM.
- The flight departs tomorrow.
In all of these cases, the present indefinite tense is used because the action is either a regular occurrence, a fact, or something that’s not expected to change.
Present Indefinite Tense Formula
The Present Indefinite Tense (also called Simple Present Tense) is used to describe habitual actions, general truths, and facts. Here are the formulas for different types of sentences:
1. Affirmative Sentences
Formula:
🔹 Subject + V1 (base form) + s/es (if subject is he/she/it) + Object
✅ Examples:
- She writes a letter.
- They play football.
2. Negative Sentences
Formula:
🔹 Subject + do/does + not + V1 + Object
✅ Examples:
- He does not like tea.
- We do not watch TV.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Formula:
🔹 Do/Does + Subject + V1 + Object + ?
✅ Examples:
- Does she write a letter?
- Do they play football?
4. Negative Interrogative Sentences
Formula:
🔹 Do/Does + Subject + not + V1 + Object + ?
(Or)
🔹 Don’t/Doesn’t + Subject + V1 + Object + ?
✅ Examples:
- Does she not write a letter? (formal)
- Doesn’t she write a letter? (informal)
Would you like more examples or explanations? 😊
Present indefinite tense rules
Rules of Present Indefinite Tense (Simple Present Tense)
The Present Indefinite Tense follows specific rules related to subject-verb agreement, negation, and question formation. Here are the key rules:
1. Subject-Verb Agreement
✅ Use the base verb (V1) with “I,” “You,” “We,” and “They.”
✅ Add “s” or “es” to the verb if the subject is “He,” “She,” or “It.”
Examples:
- I write a letter.
- He writes a letter.
- She goes to school.
📝 When to add “es” instead of “s”
- If the verb ends in -o, -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z, add “es” instead of “s.”
✅ Examples:- He goes to school.
- She watches TV.
- It passes through the tunnel.
2. Negative Sentences
✅ Use “do not (don’t)” with I, You, We, They.
✅ Use “does not (doesn’t)” with He, She, It.
✅ Do not add “s/es” to the verb in negative sentences.
Examples:
- I do not like tea.
- She does not play football. (❌ She does not plays)
Interrogative Sentences
✅ Start with “Do” for I, You, We, They.
✅ Start with “Does” for He, She, It.
✅ Use the base form of the verb (V1) after “do/does.”
Examples:
- Do you read books?
- Does he watch TV?
- Does she go to school?
Negative Interrogative Sentences
✅ Use “Do/Does + Subject + not + Verb + Object?”
✅ Use contractions (“Don’t/Doesn’t”) in informal speech.
Examples:
- Does she not like coffee?
- Doesn’t he play football?
Uses of Present Indefinite Tense
✅ For habitual actions or daily routines
- She wakes up early.
- We go to school every day.
✅ For general truths and facts
- The sun rises in the east.
- Water boils at 100°C.
✅ For future timetables and fixed schedules
- The train leaves at 9 AM.
- The shop opens at 10 AM.
✅ For instructions and directions
- You take the first left.
- Press the button and wait.
Rule of S and ES
Rules for Adding “S” and “ES” to Verbs in the Present Indefinite Tense
In the Present Indefinite Tense, we add “s” or “es” to the verb when the subject is He, She, or It (third-person singular).
✅ Rule 1: Add “S” to Most Verbs
🔹 If a verb is a regular verb, simply add “s” when the subject is He, She, or It.
✅ Examples:
- He reads a book.
- She writes a letter.
- It rains in July.
✅ Rule 2: Add “ES” to Verbs Ending in -o, -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z
🔹 If a verb ends in o, s, sh, ch, x, or z, add “es” instead of just “s.”
✅ Examples:
- He goes to school. (go → goes)
- She watches TV. (watch → watches)
- He misses the bus. (miss → misses)
- She fixes the car. (fix → fixes)
✅ Rule 3: If a Verb Ends in “Y”
🔹 If a verb ends in a consonant + “y,” change “y” to “i” and add “es.”
✅ Examples:
- He studies every day. (study → studies)
- She carries a bag. (carry → carries)
- The baby cries at night. (cry → cries)
❌ Exception: If the verb ends in a vowel + “y,” just add “s.”
✅ Examples:
- He plays cricket. (play → plays)
- She buys fruits. (buy → buys)
Interrogative Sentences
In the Present Indefinite Tense, interrogative sentences (questions) are formed using “Do” or “Does” at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject and the base verb (V1).
✅ Formula for Interrogative Sentences:
🔹 Do/Does + Subject + V1 (Base Form) + Object + ?
✅ Rules for Interrogative Sentences:
1️⃣ Use “Do” with I, You, We, They.
2️⃣ Use “Does” with He, She, It.
3️⃣ The main verb always remains in base form (V1) (No “s” or “es” after “Does”).
| Also Check: Tense Identifying Tool by writing any sentence |
✅ Examples of Interrogative Sentences:
A) Yes/No Questions:
✅ Do you like coffee?
✅ Do they play football?
✅ Does he watch TV?
✅ Does she read books?
✅ Does it rain in summer?
B) WH-Questions (Using What, Where, When, Why, Who, How, etc.)
🔹 WH-word + Do/Does + Subject + V1 + Object + ?
✅ Where do you live?
✅ What does he eat for breakfast?
✅ Why do they study English?
✅ When does the train arrive?
✅ How do birds fly?
Negative Sentences
In Present Indefinite Tense, we form negative sentences using “do not” (don’t) or “does not” (doesn’t) before the base verb (V1).
🔹 Formula for Negative Sentences
✅ For I, You, We, They:
👉 Subject + do not (don’t) + V1 + object
✅ For He, She, It:
👉 Subject + does not (doesn’t) + V1 + object
📝 Note:
- The main verb remains in its base form (V1) after “do not” or “does not.”
- We do not add “s” or “es” to the verb in negative sentences.
🔹 Examples of Negative Sentences
✅ With “do not” (don’t) (for I, You, We, They)
- I do not like coffee.
- You do not play football.
- We do not watch TV.
- They do not go to school on Sundays.
✅ With “does not” (doesn’t) (for He, She, It)
- He does not eat meat. (❌ He does not eats)
- She does not read novels.
- It does not rain in summer.
Interro-negative Sentences
Interrogative-negative sentences in the Present Indefinite Tense are questions that also express negation (not).
🔹 Formula for Interrogative-Negative Sentences
1️⃣ Do/Does + Subject + not + V1 + Object + ?
2️⃣ Don’t/Doesn’t + Subject + V1 + Object + ? (Informal)
📝 Note:
- Use “Do” with I, You, We, They
- Use “Does” with He, She, It
- The main verb remains in its base form (V1)
- “Don’t” and “Doesn’t” are used in informal speech
🔹 Examples of Interrogative-Negative Sentences
✅ Formal (Do/Does + Subject + not + V1 + Object?)
- Do you not like tea?
- Does she not play football?
- Does he not study regularly?
- Do they not go to school on Sundays?
✅ Informal (Don’t/Doesn’t + Subject + V1 + Object?)
- Don’t you like tea?
- Doesn’t she play football?
- Doesn’t he study regularly?
- Don’t they go to school on Sundays?
2. Past Indefinite Tense
The past indefinite tense, also known as the simple past tense, is used to describe an action or event that occurred and was completed in the past. Here are some rules for using the past indefinite tense:
Recognition of Past Indefinite Tense in English
S + 2nd form of Verb + O
First of all, subject is placed at the start of sentence then 2nd form of verb and object at the end with full stop.
| S | IIV | O |
| He | ate | bread |
| S | IIV | O |
| Moosa | ate | food |
| S | IIV | O |
| I | went | England |
Note: In this tense, we will not add “s” or “es” at the end of verb.
Past Indefinite Affirmative Sentences
S + IIV + O
The past indefinite tense, also known as the simple past tense, is used to describe an action that took place in the past and is now completed. In Urdu, the structure of the past indefinite tense is as follows:
| S | IIV | O |
| We | played | cricket |
We played cricket.
| S | IIV | O |
| You | drove | a car |
You drove a car.
Negative Sentence of Past Indefinite Tense
To make a sentence negative, add only “did not “right after subject. Let us formulate it.
S + did not + 1V + O.
Rule: After adding ‘did not’, IIV will be replaced with 1V
| S | did not | 1V | O |
| He | did not | go | school |
He did not go to school.
| S | did not | 1V | O |
| Ali and Amir | did not | tell | a lie |
Amir and Ali did not tell a lie.
Interrogative Sentence of Past Indefinite Tense
Did + S + 1V + O + ?
Rule: After adding ‘did’ at the start, IIV will be replaced with 1V
| Did | S | 1V | O? |
| Did | Aamir | go | market? |
Did he go to the market?
| Did | S | 1V | O? |
| Did | they | do | homework? |
Did they do homework?
Interro-Negative Sentence of Past Indefinite Tense
S + II V + O (Simple)
S + did not +IV + O (-ve)
Now Interro-negative Sentence
Did + S + not +1V + O?
| Did | S | not | 1V | O? |
| Did | they | not | go | school? |
Did they not go school?
| Did | S | not | 1V | O? |
| Did | they | not | do | homework? |
Did they not do homework?
Past Indefinite Tense Exercise
- He worked in the education department. (Affirmative)
- He did not work in the education department. (Negative)
- Did he work in the education department? (Interrogative)
- Did he not work in the education department? Or
- Didn’t he work in the education department? (Interro-negative)
- They put in great effort every time.
- They did not put in great effort every time.
- Did they put in great effort every time?
- Did they not put in great effort every time? Or
- Didn’t they put in great effort every time?
- You loved to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza.
- You did not love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza.
- Did you love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza?
- Did you not love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza? Or
- Didn’t you love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza?
- We sat in the sunshine after job time.
- We did not sit in the sunshine after job time.
- Did we sit in the sunshine after job time?
- Did we not sit in the sunshine after job time? Or
- Didn’t we sit in the sunshine after job time?
The tense identifying tool tells you the tense. Just type any tense in the search box, and it will tell the sentence belongs to which tense.
Tense Identifier Tool Tense Identifier
3. Future Indefinite Tense
In this tense anything is done, happened, or borne in future or coming times.
Recognition of Future Indefinite Tense in English
They will go to school.
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence then will or shall, the first form of the verb, and the object at the end with a full stop.
Important: We shall place shall after I and We whereas will after every subject like you, he, she, Aamir, they, etc.
Examples
He will take tea.
We shall do our duty.
I shall go to school.
Moosa will study a book.
They will travel to Lahore.
Examples
| S | will/shall | IV | O |
| I | shall | go | school |
I shall go to school.
I will go to school.
| S | will/shall | 1V | O |
| You | will | write | a letter |
You will write a letter.
You shall write a letter.
Exercise:
| S | Will/shall | IV | O |
| We | shall | play | cricket |
We shall play cricket
| S | will/shall | IV | O |
| You | will | drive | a car |
You will drive a car.
Negative Sentences of Future Indefinite Tense
To make a negative sentence, add “not” right after the helping verb (will/shall).
S+will/shall+not+1V+O
| S | will not | IV | O |
| Hamza | will not | go | school |
Hamza will not go to school.
| S | will not | IV | O |
| We | shall not | do | homework |
We shall not do homework.
Interrogative Sentences of Future Indefinite Tense
To make a sentence interrogative, place “
Shall +S+IV+O
| Will | S | IV | O? |
| Will | he | go | school |
Will he go school?
| Shall | S | IV | O? |
| Shall | we | do | homework? |
Shall we do homework?
Interro-negative Sentences
To make a sentence interro-negative, place
Shall /will+ S+not+1V+O
| Will | S | not | IV | O? |
| Will | she | not | go | school? |
Will she not go to school?
| Will | S | not | IV | O? |
| Will | this boy | not | do | homework? |
Will this boy not do homework?
Future Indefinite Tense Exercise
There are many examples of the Future Indefinite Tense having affirmative, negative, interrogative, and interro-negative sentences and each sentence has these three converted sentences in every paragraph of the five sentences below. So, you can find any sentence converted into negative, interrogative, and interro-negative sentences.
- He will work in the education department. (Affirmative)
- He will not work in the education department. (Negative)
- Will he work in the education department? (Interrogative)
- Will he not work in the education department? Or
- Won’t he work in the education department? (Interro-negative)
- They will put in great effort every time.
- They will not put in great effort every time.
- Will they put in great effort every time?
- Will they not put in great effort every time? Or
- Won’t they put in great effort every time?
- You will love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza.
- You will not love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza.
- Will you love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza?
- Will you not love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza? Or
- Won’t you love to eat Chicken Tikka Pizza?
- We will sit in the sunshine after job time.
- We will not sit in the sunshine after job time.
- Will we sit in the sunshine after job time?
- Will we not sit in the sunshine after job time? Or
- Won’t we sit in the sunshine after job time?
- My children will love to do homework together.
- My children will not love to do homework together.
- Will my children love to do homework together?
- Will my children not love to do homework together? Or
- Won’t my children love to do homework together?
- The led TV will give clearer video than the old television.
- The led TV will not give clearer video.
- Will led TV give clear video?
- Will led TV not give clear video? Or
- Won’t led TV give clear video?
4. Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense (also called the Present Progressive Tense) is used to describe actions happening right now or around the present time. It can also indicate future plans in some cases.
The Present Continuous Tense is used to express an action that is happening at the moment of speaking or a temporary action that is ongoing.
Subject + is/am/are + verb (-ing) + object
- She is reading a book. (Happening now)
- They are playing football. (Ongoing action)
- I am traveling to London next week. (Planned future action)
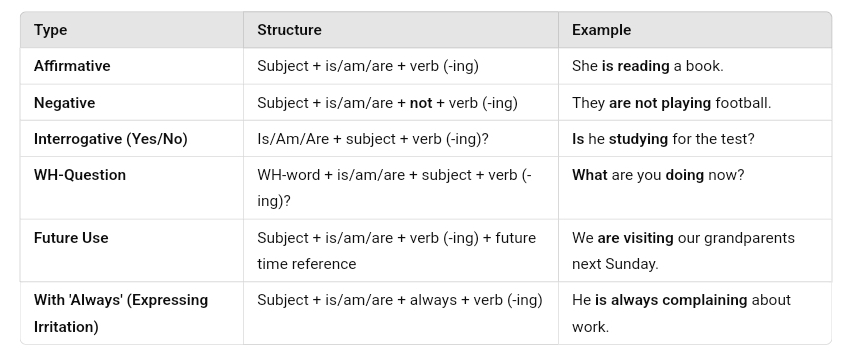
What is the Rule for Present Continuous Tense?
The Present Continuous Tense follows a specific structure and is used in different situations.
1. Structure (Formula):
Affirmative:
Subject + is/am/are + verb (-ing) + object
- She is studying for the exam.
- We are watching a movie.
Negative:
Subject + is/am/are + not + verb (-ing) + object
- He is not sleeping now.
- They are not playing football.
Interrogative:
Is/Am/Are + subject + verb (-ing) + object?
- Is she cooking dinner?
- Are they coming to the party?
2. Rules for Usage:
- Ongoing Actions (Happening Now)
- Used for actions happening at the moment of speaking.
- Example: She is talking on the phone.
- Temporary Actions
- Used for actions happening around the present time but not necessarily at the exact moment.
- Example: I am reading an interesting novel these days.
- Future Plans
- Used for fixed future arrangements.
- Example: We are visiting our grandparents next weekend.
- Changing or Developing Situations
- Used for gradual changes or trends.
- Example: The climate is getting warmer.
- Repeated Actions with “Always” (Expressing Irritation)
- Used to show something happens repeatedly (often with “always” or “constantly”).
- Example: He is always complaining about work.
3. Spelling Rules for Adding ‘-ing’
| Base Verb | Rule | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Play → Playing | Just add “-ing” | I am playing. |
| Make → Making | Drop the final -e before adding “-ing” | She is making a cake. |
| Run → Running | Double the last consonant if the verb ends in CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) | They are running fast. |
| Lie → Lying | Change -ie to -y and add “-ing” | He is lying on the bed. |
What are 20 examples of present continuous tense with answers?
Here are 20 examples of Present Continuous Tense with answers:
1. Affirmative Sentences
- She is reading a book.
- They are playing football in the park.
- I am watching a movie right now.
- He is writing an email to his boss.
- We are learning English.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully.
- The sun is shining brightly.
- My friends are coming over for dinner.
- She is baking a cake in the kitchen.
- The kids are playing outside.
2. Negative Sentences
- I am not feeling well today.
- She is not talking to anyone.
- They are not watching TV.
- He is not studying for his exams.
- We are not going to the mall today.
3. Interrogative Sentences
- Are you listening to me?
- Is she cooking dinner?
- Are they playing cricket?
- Is he working on his project?
- Am I speaking too fast?
Present Continuous Tense Questions
Here are 20 Present Continuous Tense questions categorized into Yes/No Questions and WH-Questions:
1. Yes/No Questions (Answer with Yes/No)
- Are you watching TV right now?
- Is she reading a novel?
- Are they playing football in the park?
- Is he working on his project?
- Am I speaking too fast?
- Is the baby sleeping now?
- Are we going to the shopping mall?
- Is your brother studying for the exam?
- Are the kids making a mess in the living room?
- Is the teacher explaining the lesson?
2. WH-Questions (Answer with Information)
- What are you doing right now?
- Why is she crying?
- Where are they going?
- Who is he talking to on the phone?
- What is she cooking for dinner?
- Why are they shouting so loudly?
- Which book is he reading?
- How is the weather changing these days?
- What are you thinking about?
- Why is the dog barking?
5. Past Continuous Tense
In this tense anything is done, happened or borne in past time in Continuing aspects.
They were doing their duty.
Recognition of Past Continuous Tense in English:
S + was/were +1V + ing+ O
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence then is/are/am and the first form of verb plus ‘ing’ and object at the end with a full stop.
Examples:
* 1V=1st form of verb
* 1V + ing = 4th form of verb
If the subjects are singular that is “I, He, She, It, Name”, we have to use the helping verb “was” with all of these subjects and if the subjects are plural like “You, We, They, Names”, the helping verb “were” will be used.
For He, She, It, single name= use ‘was’ as helping verb
They, You, we, plural name= use ‘were’ as helping verb
Exercise:
| S | was/were | 1V-ing | O |
| We | were | play+ing | cricket |
We were playing cricket.
| S | was/were | 1V+ing | O |
| You | were | driving | a car |
You were driving a car.
| S | was/were | 1V-ing | O |
| We | were | eating | food |
We were eating food.
| S | was/were | 1V-ing | O |
| Moosa | was | eating | bread |
Moosa was eating bread.
| S | was/were | 1V-ing | O |
| Air and Asif | were | go+ing | walk |
Aamir and Asif were going for a walk.
| S | was/were | 1V-ing | O |
| They | were | writing | a new topic |
They were writing a new topic.
Negative Sentences of Past Continuous Tense
Helping Verb= was, were
To make a sentence negative, add “not” right after the ‘helping verb’ and helping verbs may be was or were. We will add ‘not’ after one of the helping verbs (was/were).
S + was/were + not + 1Ving + O
| S | was/were | not | 1V+ ing | O |
| He | was | not | go-ing | school |
He was not going to school.
| S | was/were | not | 1V+ ing | O |
| They | were | not | do-ing | homework |
They were not doing homework.
Interrogative Sentence of Past Continuous tense
To make a sentence interrogative, we need a helping verb to put it at the start of the sentence and place a sign of interrogation/question mark at the end of the sentence. Remember, without a sign of interrogation the sentences will be considered incomplete or wrong. Also, do not place a full stop after a question mark.
| Was/Were | S | 1v+ing | O |
| Was | Was | going | school? |
Was he going to school?
| Was/Were | S | 1V+ ing | O? |
| Were | they | doing | homework? |
Were they doing homework?
Interro-negative Sentence of Past Continuous Tense
To make a sentences interro-negative, it is an easy way that makes this sentence negative first then place helping verb at the start of the sentence and place question mark at the end.
S + Was/Were + 1V ing + O
S + Was/Were + not + 1V ing + O (Negative)
Was/Were + S + not + 1V ing + O ? (Interro-negative)
| Was/Were | S | not | 1V+ ing | O? |
| Was | he | not | go-ing | school? |
Was he not going school?
| Was/Were | S | not | 1V+ ing | O? |
| Were | they | not | do-ing | homework? |
Were they not doing homework?
Past Continuous Tense When and While
In the past continuous tense, “when” and “while” are commonly used to describe two past actions happening at the same time or when one action interrupts another. Here’s how they function:
1. “When” with Past Continuous & Simple Past
- “When” introduces a shorter action (Simple Past) that interrupts a longer action (Past Continuous).
- Structure:
Past Continuous + when + Simple Past
OR
Simple Past + when + Past Continuous - Examples:
- I was watching TV when the phone rang.
- She was cooking dinner when the lights went out.
2. “While” with Two Past Continuous Actions
- “While” is used when two longer actions were happening at the same time.
- Structure:
Past Continuous + while + Past Continuous - Examples:
- I was reading a book while she was listening to music.
- They were playing football while we were watching them.
3. “While” with Past Continuous & Simple Past
- “While” can also introduce the longer action (Past Continuous), and the shorter action (Simple Past) happens during it.
- Structure:
While + Past Continuous, Simple Past
OR
Simple Past + while + Past Continuous - Examples:
- While I was walking to the store, I met an old friend.
- He called me while I was sleeping.
Let me know if you need more clarification!
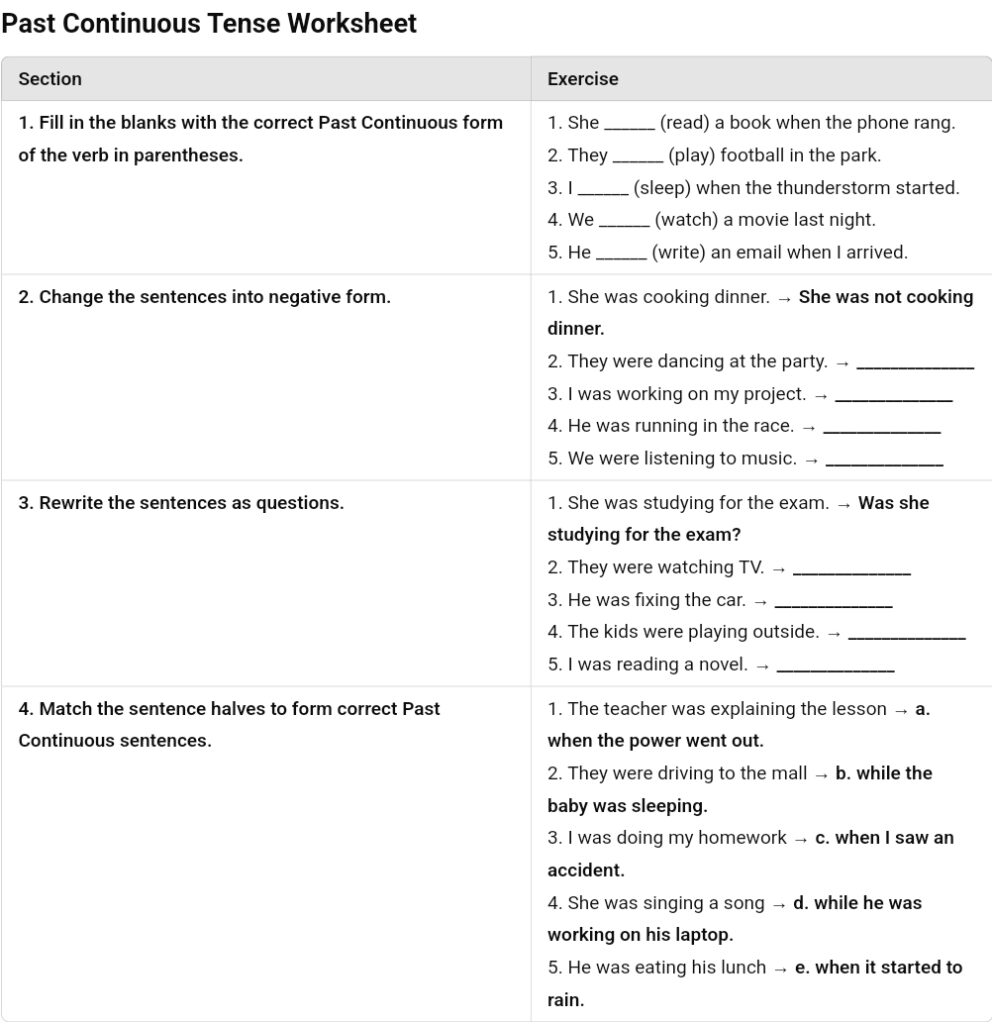
Past Continuous Tense Questions
When forming questions in the past continuous tense, we use:
✅ Was/Were + subject + verb (-ing)?
1. Yes/No Questions
Structure:
🔹 Was/Were + subject + verb (-ing) + ?
Examples:
- Was she studying when you called? (Yes, she was. / No, she wasn’t.)
- Were they playing football in the park? (Yes, they were. / No, they weren’t.)
- Was it raining last night?
2. Wh- Questions
Structure:
🔹 Wh-word + was/were + subject + verb (-ing)?
Examples:
- What were you doing at 8 PM yesterday?
- Where was she going when you saw her?
- Why were they laughing so loudly?
- Who was she talking to on the phone?
3. Negative Questions
Structure:
🔹 Wasn’t/Weren’t + subject + verb (-ing)?
Examples:
- Wasn’t he waiting for you?
- Weren’t they watching the match?
Negative questions are often used for confirmation or surprise.
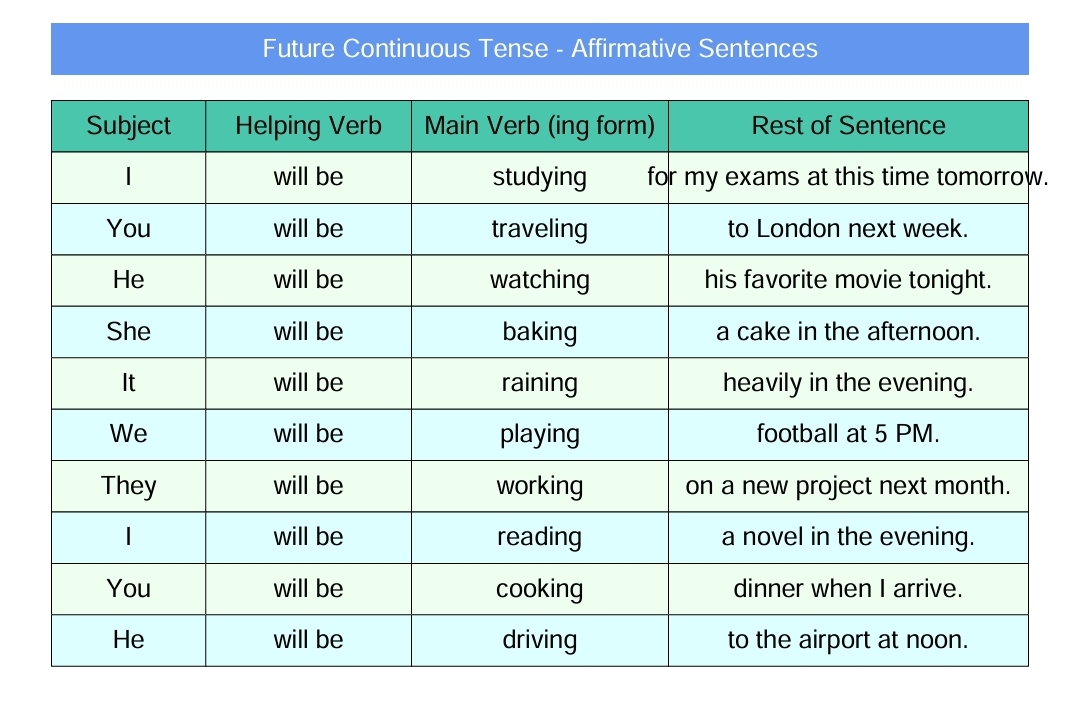
6. Future Continuous Tense
In this tense anything is done, happened, or borne in future or coming times in Continuous aspects.
Basically, there are three basic contents in any sentence.
They will be going their duties.
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence then will be or shall be, the first form of the verb with “ing” (a fourth form of the verb) and object at the end with a full stop.
Important: We shall place “shall be” after “I” and “We” whereas “will be” after every subject like you he, she, Aamir, they, etc.
Examples of Future Continuous Tense
He will be going abroad.
We shall be eating food.
I shall be going to school.
Moosa will be studying a book.
They will be traveling to Lahore.
Change “shall be” into “will be” and “will be” change into “shall be” if there is needed to give a must touch.
Will be ➡️ shall be
Shall be ➡️ will be
Examples
| S | will/shall | be | 1V | ing | O |
| We | shall | be | Play | ing | cricket |
We shall be playing cricket.
| S | will/shall | be | 1V | ing | O |
| You | will | be | bath | ing | canal |
You will be bathing in a canal.
| S | will/shall | be | 1V | ing | O |
| I | will | be | go | ing | school |
I shall be going to school.
| S | will/shall | be | 1V | ing | O |
| You | Shall | be | going | ing | school |
You will be bathing in the canal.
| S | will/shall | be | 1V | ing | O |
| You | will | be | write | ing | letter |
You will be writing a letter.
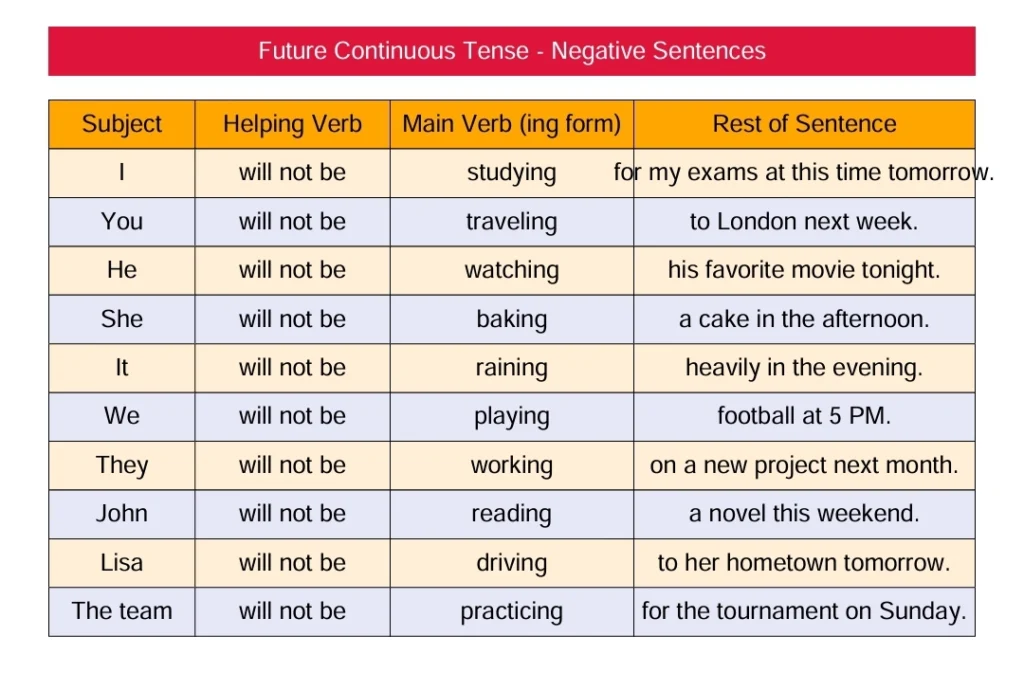
Negative Sentences of Future Continuous Tense
To make a sentence negative, add “not” right after the helping verb “will”.
Formula of Negative Sentence of Future Continuous Tense
S + will/shall + not + 1V ing + O
Examples:
| S | will/shall | not | be | 1V | ing | O |
| He | will | not | be | go | ing | school |
He will not be going to school.
Interrogative Sentence of Future Continuous Tense
| S | will/shall | not | be | 1V | ing | O |
| They | will | not | be | do | ing | homework |
They will not be doing homework.
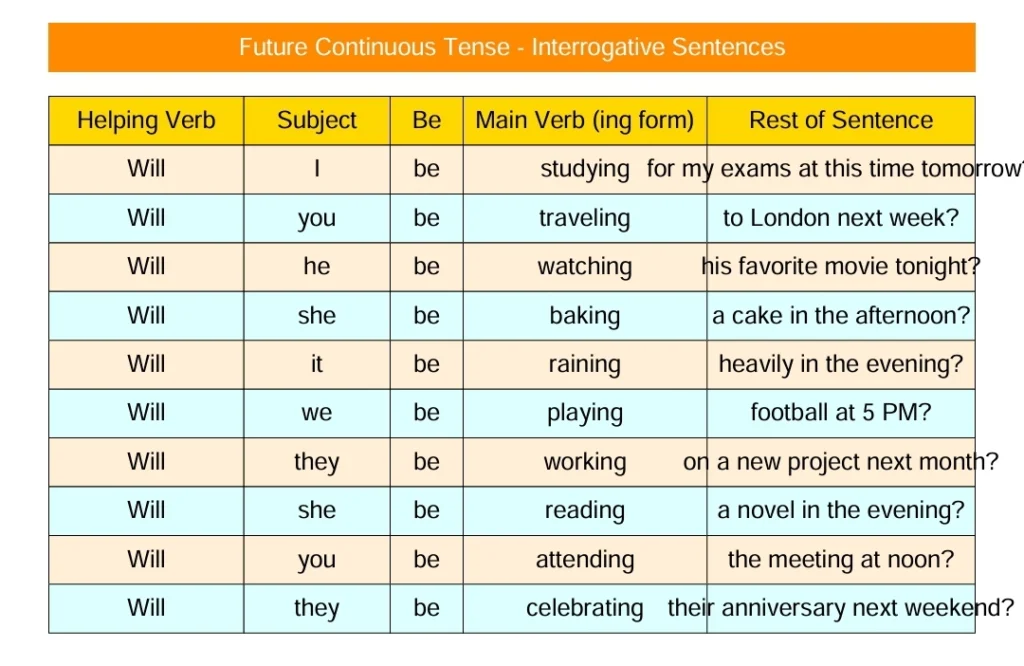
To make the sentence of Future Continuous Tense interrogative, place “helping verb” at the start of the sentence and add a question mark at the end. Let us formulate:
Will/Shall + S + be + 1V ing + O ?
| Will/shall | S | be | 1V | ing | O? |
| Will | he | be | go | ing | school? |
Will he be going to school?
| Will/shall | S | be | 1V | ing | O? |
| Will | they | be | do | ing | homework? |
Will they be doing homework?
Interro-negative Sentences of Future Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interro-negative, first, make it negative and finally place the helping verb at the start of the sentence and end it by adding a question mark.
S + will /shall + be+1V + O (simple)
S + will /shall not + be+1V + O (-ve)
Now Interronegative Sentence:

Will /Shall + S + not + be+1V + O?
| Will/shall | S | not | be | 1V | ing | O? |
| Shall | I | not | be | go | ing | school? |
Shall I not be going to school?
| Will/shall | S | not | be | 1V | ing | O? |
| Will | they | not | be | do | ing | homework? |
Will they not be doing homework?
7. Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions or situations that have occurred at an unspecified time before the present or actions that started in the past and continue into the present. It often connects the past with the present.
Recognition in English
S +has/have+ 3rd form of Verb + O
They have done their duty.
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence, then the 3rd form of the verb, and the object at the end with a full stop.
Examples
* 3V=3rd form of the verb
has=He, She, It or singular name
have=I, We, They, You or plural name
S + has/have+ 3V + O
| S | has/have | 3V | O |
| We | have | played | cricket |
We have played cricket.
| S | has/have | 3V | O |
| You | have | driven | car |
You have driven a car.
Present Perfect Tense Exercise
In this portion, we’ll learn all types of sentence examples.
Affirmative Sentences
The affirmative sentences are also called positive or general sentences. Here are 10 examples of affirmative sentences present perfect tense:

Negative Sentences
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after has or have. Let us formulate it.
S + has /have not +3V + O
| S | has/have | not | 3V | O |
| He | has | not | gone | school |
He has not gone to school.
| S | has/have | not | 3V | O |
| They | have | not | done | homework. |
They have not done homework.
Interrogative Sentence
To make a sentence interrogative, place “has” or “have” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Has / Have + S + 3V + O + ?
| Has/have | S | 3V | O? |
| Has | Ali | gone | school? |
Has Ali gone to school?
| Has/have | S | 3V | O? |
| Have | they | done | school work? |
Have they done school work?
Interro-Negative Sentence
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “has“ or “ have” right before the subject of a negative sentence and put the sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
S +has/have +3V + O (Simple)
S +has /have not +3V + O (-ve)
Now Interronegative Sentence
Has /Have + S + not +3V + O?
| Has/have | S | not | 3V | O? |
| Have | Asif and Ali | not | gone | school? |
Have Asif and Ali not gone to school?
| Has/have | S | not | 3V | O? |
| Have | you | not | done | homework? |
Have you not done homework?
Present Perfect Tense Sentences Examples of All Sentences
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative | Interro-Negative |
|---|---|---|---|
| She has finished her homework. | She has not finished her homework. | Has she finished her homework? | Has she not finished her homework? |
| I have visited Paris twice. | I have not visited Paris twice. | Have I visited Paris twice? | Have I not visited Paris twice? |
| They have bought a new car. | They have not bought a new car. | Have they bought a new car? | Have they not bought a new car? |
| He has written three books. | He has not written three books. | Has he written three books? | Has he not written three books? |
| We have known each other for ten years. | We have not known each other for ten years. | Have we known each other for ten years? | Have we not known each other for ten years? |
| The movie has started already. | The movie has not started already. | Has the movie started already? | Has the movie not started already? |
| She has just arrived at the airport. | She has not just arrived at the airport. | Has she just arrived at the airport? | Has she not just arrived at the airport? |
| I have never seen such a beautiful sunset. | I have not seen such a beautiful sunset. | Have I seen such a beautiful sunset? | Have I not seen such a beautiful sunset? |
| They have completed the project successfully. | They have not completed the project successfully. | Have they completed the project successfully? | Have they not completed the project successfully? |
| He has broken his phone again. | He has not broken his phone again. | Has he broken his phone again? | Has he not broken his phone again? |
8. Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action or a specific time in the past. It emphasizes that one event happened before another in the past.
Formula of Past Perfect Tense
S +had+ 3rd form of Verb + O
The function in any sentence is called action, and the time when the work is done is called action, whereas the work on which it is done is called object.
They had done their duty.
In this sentence, ‘they’ are doing their duty. So, ‘they’ will be the subject. The work is being done on ‘duty’, so, it is ‘an object’. Meanwhile, ‘done’ is a verb that is called a tense/verb.
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence, then 3rd form of the verb followed by “had” and the object at the end with a full stop.
Examples* 3V=3rd form of verb
Whatever the subject is, ‘had’ will act as a helping verb.
S + had+ 3V + O
| S | had | 3V | O |
| He | had | eaten | bread. |
S + had + 3V + O
| S | had | 3V | O |
| They | had | Played | cricket. |
S + has + 3V + O
| S | had | 3V | O |
| Ali and Hamza | had | Written | homework. |
Recognizing the Tense
We can recognize this sentence by finding ‘had’ right after the subject.
Exercise
| S | had | 3V | O |
| We | had | played | cricket. |
We had played cricket.
| S | had | 3V | O |
| You | had | driven | a car. |
You had driven a car.
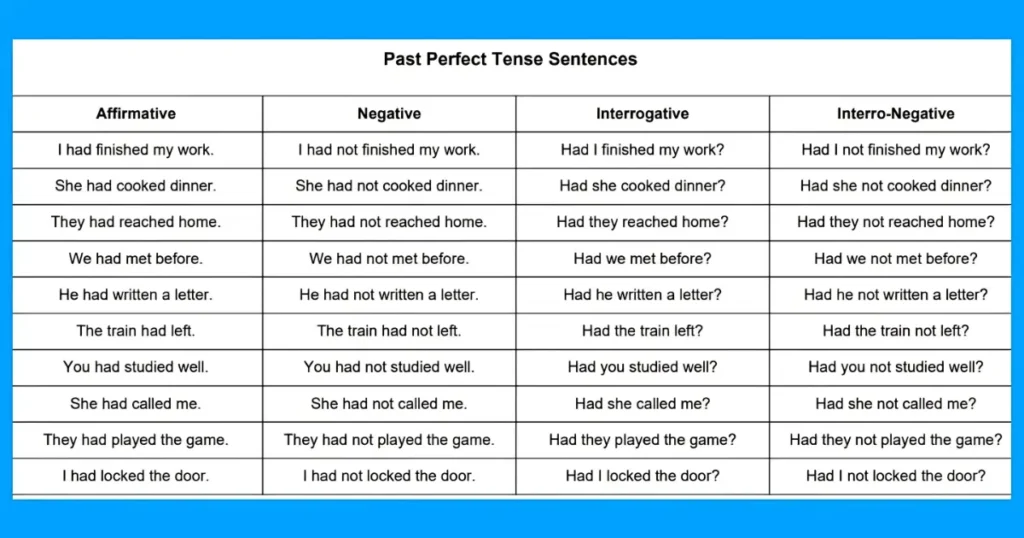
Negative Sentences of Past Perfect Tense
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after had. Let us formulate it.
S + had + not +3V + O
Negative Sentences of Past Perfect Tense
| S | had | not | 3V | O |
| He | had | not | gone | school |
He had not gone school.
| S | had | not | 3V | O |
| They | had | not | done | homework. |
They had not done homework.
Interrogative Sentence
To make a sentence interrogative, place “had” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Had + S + 3V + O + ?
Examples of Past Perfect Tense Interrogative Sentences
| Had | S | 3V | O? |
| Had | he | gone | school? |
Had he gone to school?
| Had | S | 3V | O? |
| Had | they | done | homework? |
Had they done homework?
Interro-Negative Sentences
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “ had” right before the subject of a negative sentence and put the sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
S +had +3V + O (Simple)
S + had+ not +3V + O (-ve)
Examples of Past Perfect Tense Interrogative Sentences
Now, the Interronegative Sentence will be as:
Had + S+not +3V + O?
| Had | S | not | 3V | O? |
| Had | you | not | gone | abroad? |
Had you not gone abroad?
| Had | S | not | 3V | O? |
| Had | they | not | done | homework? |
Had they not done homework?
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some important questions related to past perfect tense the students may have in their minds to ask.
1. Past Perfect Tense Ks2
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that happened before another past event. It helps show which event happened first.
Structure:
✅ Subject + had + past participle
Examples for KS2:
- I had finished my homework before dinner.
- She had baked a cake before the guests arrived.
- We had already left when it started raining.
- The train had departed before we got to the station.
- He had never seen a lion before visiting the zoo.
How It Works:
- The past perfect action happens first.
- The simple past action happens after it.
Example:
✅ I had eaten (past perfect) before my friend arrived (simple past).
9. Future Perfect Tens
In this tense, anything will be done, happened, or borne in future complete aspects.
Structure of Future Perfect Tense
S +will/shall + have+ 3rd form of Verb + O
First of all, the subject is placed at the start of the sentence, then will have or shall have the 3rd form of verb and object at the end with a full stop.
They will have done their duty.
Remember: ‘Will have’ will come after You, He, She, It, They, Name(s) whereas ‘shall have’ come after I and We.
Examples of Future Perfect Tense Affirmative Sentences
| S | will/shall | have | 3V | O |
| Moosa | will | have | eaten | bread. |
Exercise:
| S | shall | have | 3V | O |
| We | shall | have | played | cricket |
We shall have played cricket.
| S | Will/shall | have | 3V | O |
| You | will | have | driven | a car |
You will have driven a car.
Here are 20 more unique examples of future perfect tense in affirmative sentences, formatted in a table:
| No. | Sentence |
|---|---|
| 1. | By next year, she will have completed her master’s degree. |
| 2. | By 10 PM, they will have finished their dinner. |
| 3. | By the time you arrive, I will have cleaned the house. |
| 4. | By next summer, we will have visited five countries. |
| 5. | By December, he will have worked at the company for ten years. |
| 6. | By tomorrow morning, the rain will have stopped. |
| 7. | By the end of the month, she will have saved enough money for a new car. |
| 8. | By noon, the chef will have prepared all the dishes. |
| 9. | By next week, the workers will have completed the project. |
| 10. | By the end of the year, they will have planted 500 trees. |
| 11. | By 5 PM, I will have submitted my assignment. |
| 12. | By the time the train arrives, she will have packed her luggage. |
| 13. | By the age of 30, he will have written three novels. |
| 14. | By next month, the company will have launched its new product. |
| 15. | By the time we reach home, dad will have cooked dinner. |
| 16. | By the time school reopens, the students will have completed their vacation homework. |
| 17. | By next Friday, I will have finished reading this book. |
| 18. | By 2026, scientists will have discovered more planets. |
| 19. | By the time you wake up, I will have left for work. |
| 20. | By the time she returns, they will have decorated the house. |
Each sentence is unique and demonstrates the future perfect tense clearly. Let me know if you need more examples or variations!
Future Perfect Tense Negative Sentences
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after will or shall. There are two helping verbs in this tense, but we shall use the first helping verb will/shall to make a sentence negative. Let us formulate it:
Examples of Future Perfect Tense Negative Sentences
S + will/shall +not +have +3V + O
| S | will/shall | not | have | 3V | O |
| He | will | not | have | gone | school. |
He will not have gone to school.
| S | will/shall | not | have | 3V | O |
| They | will | not | have | done | homework. |
They will not have done homework.
| No. | Negative Sentence (Future Perfect Tense) |
|---|---|
| 1. | She will not have finished her homework by 8 PM. |
| 2. | They will not have arrived at the airport before noon. |
| 3. | He will not have completed his project by the deadline. |
| 4. | We will not have eaten dinner before the movie starts. |
| 5. | The train will not have left the station before we get there. |
| 6. | I will not have written the report by tomorrow morning. |
| 7. | You will not have learned French by next year. |
| 8. | The shop will not have opened by 6 AM. |
| 9. | The children will not have finished their exams before the holidays begin. |
| 10. | She will not have reached home by midnight. |
| 11. | They will not have saved enough money to buy a car by December. |
| 12. | The doctor will not have arrived at the hospital before the emergency case. |
| 13. | He will not have fixed the car by the weekend. |
| 14. | We will not have packed our bags before the taxi arrives. |
| 15. | The baby will not have fallen asleep before 10 PM. |
| 16. | I will not have completed the book by the end of the month. |
| 17. | The guests will not have left before sunrise. |
| 18. | She will not have finished baking the cake before the party starts. |
| 19. | They will not have repaired the road before the monsoon season. |
| 20. | He will not have submitted the assignment by Friday. |
Each of these sentences correctly follows the Future Perfect Negative structure:
Subject + will not have + past participle + rest of the sentence.
Future Perfect Tense Interrogative Sentences
To make a sentence interrogative, place “will” or “shall” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence and place a question mark at the end. Let us formulate it.
Examples of Future Perfect Tense Interrogative Sentences
Will / Shall + S + have 3V + O + ?
| Will/Shall | S | have | 3V | O? |
| Will | he | have | gone | school? |
Will he have gone to school?
| Will/Shall | S | have | 3V | O? |
| Will | they | have | done | homework? |
Will they have done homework?
Here’s a table with 20 unique interrogative sentences in the Future Perfect Tense:
| No. | Interrogative Sentence (Future Perfect Tense) |
|---|---|
| 1. | Will she have finished her project by tomorrow? |
| 2. | Will they have reached the airport before midnight? |
| 3. | Will he have completed his assignment by the deadline? |
| 4. | Will we have saved enough money for the trip by next year? |
| 5. | Will the train have left by the time we arrive? |
| 6. | Will she have learned French before moving to Paris? |
| 7. | Will the students have submitted their reports by Friday? |
| 8. | Will you have read the entire book by next week? |
| 9. | Will the builders have finished constructing the house by December? |
| 10. | Will the sun have set by the time we reach the beach? |
| 11. | Will the scientists have discovered a cure for the disease by 2030? |
| 12. | Will he have recovered from his illness by next month? |
| 13. | Will she have written her thesis before the final submission date? |
| 14. | Will we have completed our training by the end of the year? |
| 15. | Will you have cooked dinner before they arrive? |
| 16. | Will the company have launched its new product by next quarter? |
| 17. | Will the teacher have graded all the papers by Monday? |
| 18. | Will the guests have arrived before the ceremony begins? |
| 19. | Will they have fixed the road before the festival starts? |
| 20. | Will you have achieved your goals by the time you turn 30? |
These sentences follow the Future Perfect Tense structure:
Will + subject + have + past participle + (time reference)?
Interro-Negative Sentence of Future Perfect Tense
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “Will” or “Shall” right before the subject of a negative sentence and put the sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
S +will/shall + have +3V + O (Simple)
S +will/shall + not + have 3V + O (-ve)
Now Interronegative Sentence
Will/Shall+ S+not +have 3V + O?
Examples of Future Perfect Tense Interro-negative Sentences
| Will/Shall | S | not | have | 3V | O? |
| Will | she | not | have | gone | school? |
Will she not have gone to school?
| Will/Shall | S | not | have | 3V | O? |
| Shall | we | not | have | done | homework? |
Shall we not have done homework?
| No. | Interro-Negative Sentence (Future Perfect Tense) |
|---|---|
| 1. | Will they not have completed the project by tomorrow? |
| 2. | Will she not have cooked dinner before we arrive? |
| 3. | Will you not have finished your homework by 8 PM? |
| 4. | Will he not have left for the airport by noon? |
| 5. | Will they not have written the report by next week? |
| 6. | Shall we not have reached the station by 10 AM? |
| 7. | Will she not have learned Spanish by the end of the year? |
| 8. | Will he not have submitted his assignment before the deadline? |
| 9. | Will you not have read the book by next Monday? |
| 10. | Will they not have built the new house by December? |
| 11. | Will she not have completed her studies by next year? |
| 12. | Shall we not have solved all the questions before the exam ends? |
| 13. | Will he not have repaired the car by the evening? |
| 14. | Will they not have arrived at the hotel before midnight? |
| 15. | Will you not have packed your bags before the trip? |
| 16. | Will she not have finished painting the room by morning? |
| 17. | Shall we not have watered the plants before the sun rises? |
| 18. | Will he not have learned to drive by the end of summer? |
| 19. | Will they not have delivered the package by Friday? |
| 20. | Will you not have booked the tickets before the prices go up? |
“Shall not” is used with “we” in formal contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions for Future Perfect Tense
Here are some important questions related to future perfect tense.
what is the verb tense and aspect for Past Perfect, Future Perfect, Past Progressive, and Future Progressive?
The verb tense refers to when an action occurs (past or future), and the aspect describes whether the action is completed, ongoing, or habitual. Here’s how the four tenses you mentioned are categorized:
| Tense & Aspect | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Past Perfect (Completed action before another past event) | Had + past participle | She had finished the report before the meeting started. |
| Future Perfect (Completed action before a future event) | Will have + past participle | They will have completed the project by next week. |
| Past Progressive (Ongoing action in the past) | Was/were + present participle (-ing) | He was studying when she called. |
| Future Progressive (Ongoing action in the future) | Will be + present participle (-ing) | She will be traveling at this time tomorrow. |
Each combination gives a different meaning based on whether the action is complete (perfect aspect) or ongoing (progressive aspect). Let me know if you need more clarification!
What are the key words for future perfect tense?
The future perfect tense is often used with specific time-related expressions that indicate a deadline or a point in the future before which the action will be completed.
Key Words for Future Perfect Tense:
1. Time Expressions:
- By + specific time (by tomorrow, by next year, by 2025, by 5 PM)
- By the time (by the time you arrive, by the time the movie starts)
- Before + specific time/event (before Monday, before summer ends)
- Until + point in the future (until next week, until 2030)
2. Adverbs of Certainty (Optional but Common):
- Certainly, definitely, surely (He will surely have completed his work by then.)
3. Conditional Clauses:
- If + present tense (If you arrive late, the train will have left.)
Examples:
- By next week, she will have finished her assignment.
- By the time we reach the airport, the flight will have taken off.
- Before 6 PM, they will have completed the project.
- She will have learned French by the end of the year.
10. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense states an action that started in the past and is still continuing in the present time. It emphasizes the duration of the action.
S+has/have+been+1V + ing+ O.
They have been doing duty.
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense for Affirmative Sentences
has been =He, She, It or singular name
have been =I, We, They, You or plural name
| S | has/have | been | 1V+ing | O |
| Ahmad | has | been | do-ing | job. |
Ahmad has been doing a job.
| S | has/have | been | 1V+ing | O |
| He | has | been | do-ing | hard work. |
He has been doing hard work.
| No. | Affirmative Sentence (Present Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She has been studying for her exams all morning. |
| 2 | They have been playing football in the park. |
| 3 | He has been working on his project for three hours. |
| 4 | I have been learning Spanish for a few months. |
| 5 | The baby has been crying for a long time. |
| 6 | We have been waiting for the bus for twenty minutes. |
| 7 | The teacher has been explaining the lesson patiently. |
| 8 | John has been fixing his car for two days. |
| 9 | The chef has been cooking delicious meals. |
| 10 | The kids have been watching cartoons all evening. |
| 11 | She has been practicing the piano for hours. |
| 12 | The workers have been repairing the road all day. |
| 13 | My mother has been knitting a sweater for me. |
| 14 | The students have been discussing the topic in groups. |
| 15 | The dog has been barking at strangers. |
| 16 | He has been jogging in the park every morning. |
| 17 | I have been decorating my house for the festival. |
| 18 | The gardener has been watering the plants regularly. |
| 19 | They have been traveling across different countries. |
| 20 | The author has been writing a new novel for months. |
Negative Sentence of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after has or have. Let us formulate it.
S+has/have+not+been+4V+O
4V=1V + ing
| S | has/have | not | been | 1V+ing | O |
| We | have | not | been | go-ing | school |
We have not been going school.
| S | has/have | not | been | 1V+ing | O |
| She | has | not | been | cook-ing | food |
She has not been cooking food.
Here is a table with 20 important negative sentences in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
| No. | Negative Sentence (Present Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She has not been studying for the test. |
| 2 | They have not been working on the project. |
| 3 | He has not been exercising regularly. |
| 4 | I have not been reading that book lately. |
| 5 | We have not been waiting for too long. |
| 6 | The baby has not been crying this morning. |
| 7 | You have not been following the instructions. |
| 8 | The teacher has not been explaining the topic well. |
| 9 | She has not been practicing the piano. |
| 10 | He has not been attending his online classes. |
| 11 | They have not been traveling much this year. |
| 12 | I have not been feeling well for a while. |
| 13 | The dog has not been barking at night. |
| 14 | She has not been cooking dinner lately. |
| 15 | We have not been discussing the new plan. |
| 16 | He has not been calling his friends often. |
| 17 | The company has not been hiring new employees. |
| 18 | You have not been preparing for the meeting. |
| 19 | I have not been sleeping well these days. |
| 20 | They have not been cleaning the house properly. |
Interrogative Sentences of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interrogative, place “has” or “have” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Has / Have + S +been +1V+ing + O + ?
| Has/Have | S | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Has | Ahmad | been | do-ing | teaching job? |
Has Ahmad been doing teaching job?
| Has/Have | S | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Have | you | been | take-ing | fever medicine? |
Have you been taking fever medicine?
| No. | Interrogative Sentence (Present Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Have you been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Has she been working on her project all day? |
| 3 | Have they been playing football in the park? |
| 4 | Has he been practicing the guitar recently? |
| 5 | Have we been waiting here for too long? |
| 6 | Has it been raining heavily? |
| 7 | Have you been feeling well lately? |
| 8 | Has the dog been barking all night? |
| 9 | Have the kids been watching TV for hours? |
| 10 | Has the baby been crying a lot? |
| 11 | Have you been learning Spanish? |
| 12 | Has she been cooking dinner? |
| 13 | Have they been discussing the issue seriously? |
| 14 | Has he been reading that book? |
| 15 | Have you been exercising daily? |
| 16 | Have the workers been fixing the road? |
| 17 | Has the teacher been explaining the topic clearly? |
| 18 | Have we been talking too loudly? |
| 19 | Have they been planning their trip? |
| 20 | Has she been designing new clothes? |
Interro-Negative Sentences of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “has” or “ have“ right before the subject of a negative sentence and put a sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
(General Sentence)(Step 1)
S+has/have+been+1V+ing+O
(Negative Sentence)(Step 2)
S+has/have+not+been+1V+ing+O
(General Sentence)(Step 3)
Has/have+S+not+been+1V+O?
| Has/Have | S | not | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Has | he | not | been | go-ing | school? |
Has he not been going school?
| Has/Have | S | not | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Have | you | not | been | take-ing | fever medicine? |
Have you not been taking fever medicine?
| No. | Interro-Negative Sentence (Present Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Have you not been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Have they not been playing football since morning? |
| 3 | Have we not been waiting for the bus? |
| 4 | Have you not been learning English recently? |
| 5 | Have the children not been making noise? |
| 6 | Have the workers not been repairing the road? |
| 7 | Has she not been reading that novel? |
| 8 | Has he not been working on his project? |
| 9 | Have you not been exercising daily? |
| 10 | Have they not been traveling around the country? |
| 11 | Has the teacher not been explaining the topic? |
| 12 | Have we not been discussing this matter? |
| 13 | Have you not been watching the news? |
| 14 | Has your brother not been attending classes? |
| 15 | Have the students not been preparing for the test? |
| 16 | Have the birds not been chirping all day? |
| 17 | Has the baby not been crying for hours? |
| 18 | Has she not been cooking dinner for the family? |
| 19 | Have they not been waiting outside? |
| 20 | Have you not been writing your assignment? |
11. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe an action that started in the past, continued for a period of time, and was completed before another past action or time.
S+had+been+1V + ing+ O.
They had been doing duty.
Examples of Past Perfect Continuous Tense for Affirmative Sentences
had been =for every type of subject
| S | had | been | 1V+ing | O |
| Ahmad | had | been | do-ing | job. |
Ahmad had been doing a job.
| S | had | been | 1V+ing | O |
| He | had | been | do-ing | hard work. |
He had been doing hard work.
| No. | Affirmative Sentence (Past Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She had been studying for her exams all morning. |
| 2 | They had been playing football in the park. |
| 3 | He had been working on his project for three hours. |
| 4 | I had been learning Spanish for a few months. |
| 5 | The baby had been crying for a long time. |
| 6 | We had been waiting for the bus for twenty minutes. |
| 7 | The teacher had been explaining the lesson patiently. |
| 8 | John had been fixing his car for two days. |
| 9 | The chef had been cooking delicious meals. |
| 10 | The kids had been watching cartoons all evening. |
| 11 | She had been practicing the piano for hours. |
| 12 | The workers had been repairing the road all day. |
| 13 | My mother had been knitting a sweater for me. |
| 14 | The students had been discussing the topic in groups. |
| 15 | The dog had been barking at strangers. |
| 16 | He had been jogging in the park every morning. |
| 17 | I had been decorating my house for the festival. |
| 18 | They had been travelling across different countries. |
| 19 | They had been traveling across different countries. |
| 20 | The author had been writing a new novel for months. |
Negative Sentence of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after “had”. Let us formulate it.
S+had +not+been+4V+O
| S | had | not | been | 1V+ing | O |
| We | had | not | been | go-ing | school |
We had not been going school.
| S | had | not | been | 1V+ing | O |
| She | had | not | been | cook-ing | food |
She had not been cooking food.
| No. | Negative Sentence (Past Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She had not been studying for the test. |
| 2 | They had not been working on the project. |
| 3 | He had not been exercising regularly. |
| 4 | I had not been reading that book lately. |
| 5 | We had not been waiting for too long. |
| 6 | The baby had not been crying this morning. |
| 7 | You had not been following the instructions. |
| 8 | The teacher had not been explaining the topic well. |
| 9 | She had not been practicing the piano. |
| 10 | He had not been attending his online classes. |
| 11 | They had not been traveling much this year. |
| 12 | I had not been feeling well for a while. |
| 13 | The dog had not been barking at night. |
| 14 | She had not been cooking dinner lately. |
| 15 | We had not been discussing the new plan. |
| 16 | He had not been calling his friends often. |
| 17 | The company had not been hiring new employees. |
| 18 | You had not been preparing for the meeting. |
| 19 | I had not been sleeping well these days. |
| 20 | They had not been cleaning the house properly. |
Interrogative Sentences of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interrogative, place “had ” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Had + S +been +1V+ing + O + ?
| Had | S | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Had | Ahmad | been | do-ing | teaching job? |
Had Ahmad been doing teaching job?
| Had | S | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Had | you | been | take-ing | fever medicine? |
Had you been taking fever medicine?
Here’s a table with 20 interrogative sentences in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
| No. | Interrogative Sentence (Past Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Had you been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Had she been working on her project all day? |
| 3 | Had they been playing football in the park? |
| 4 | Had he been practicing the guitar recently? |
| 5 | Had we been waiting here for too long? |
| 6 | Had it been raining heavily? |
| 7 | Had you been feeling well lately? |
| 8 | Had the dog been barking all night? |
| 9 | Had the kids been watching TV for hours? |
| 10 | Had the baby been crying a lot? |
| 11 | Had you been learning Spanish? |
| 12 | Had she been cooking dinner? |
| 13 | Had they been discussing the issue seriously? |
| 14 | Had he been reading that book? |
| 15 | Had you been exercising daily? |
| 16 | Had the workers been fixing the road? |
| 17 | Had the teacher been explaining the topic clearly? |
| 18 | Had we been talking too loudly? |
| 19 | Had they been planning their trip? |
| 20 | Had she been designing new clothes? |
Interro-Negative Sentences of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “ Had “ right before the subject of a negative sentence and put a sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
(General Sentence)(Step 1)
S+had+been+1V+ing+O
(Negative Sentence)(Step 2)
S+had+not+been+1V+ing+O
(General Sentence)(Step 3)
Had+S+not+been+1V+O?
| Had | S | not | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Had | he | not | been | go-ing | school? |
Had he not been going school?
| Had | S | not | been | 1V+ing | O? |
| Had | you | not | been | take-ing | fever medicine? |
Had you not been taking fever medicine?
| No. | Interro-Negative Sentence (Past Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Had you not been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Had they not been playing football since morning? |
| 3 | Had we not been waiting for the bus? |
| 4 | Had you not been learning English recently? |
| 5 | Had the children not been making noise? |
| 6 | Had the workers not been repairing the road? |
| 7 | Had she not been reading that novel? |
| 8 | Had he not been working on his project? |
| 9 | Had you not been exercising daily? |
| 10 | Had they not been traveling around the country? |
| 11 | Had the teacher not been explaining the topic? |
| 12 | Had we not been discussing this matter? |
| 13 | Had you not been watching the news? |
| 14 | Had your brother not been attending classes? |
| 15 | Had the students not been preparing for the test? |
| 16 | Had the birds not been chirping all day? |
| 17 | Had the baby not been crying for hours? |
| 18 | Had she not been cooking dinner for the family? |
| 19 | Had they not been waiting outside? |
| 20 | Had you not been writing your assignment? |
Structure of Past Perfect Continuous Tense with Time
S+had+been+1V+ ing + O + since/for + time
He had been reading a book since morning.
We had been working for one year.
| S | had | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time |
For=how long
For Example:
for two years, one month, half an hour
Since morning, last Summer, night, June.
He had been reading a book since morning.
| S | had | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time |
| We | had | been | do-ing | work | for | one year |
We had been doing work for one year.
Negative Sentence for Time Frame
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after had. Let us formulate it.
S+had+been+not+4V+O+since/for+…..
| S | had | not | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time |
| We | had | not | been | play-ing | cricket | for | four years |
We had not been playing cricket for four years.
| S | had | not | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time |
| We | had | not | been | gossip-ing | – | for | four an hour |
We had not been playing cricket for four years.
| Sajid | had | not | go-ing | school | since | Wednesday |
Sajid had not been going school since Wednesday. Interrogative Sentence for Time Frame
To make a sentence interrogative, place“had“ right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Had+S+been+4V+O+since/for+…… ?
| Had | he | been | reading | a book | since | morning? |
Had he been reading a book since morning?
| Had | we | been | do-ing | work | for | one year? |
Had we been doing work for one year?
| Had | S | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time? |
| Had | Ali | been | do-ing | a job | for | two years? |
Had Ali been doing a job for two years?
Interro-Negative Sentences for Time Frame
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “had“ right before the subject of a negative sentence and put sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
S+had+been+not+1Ving+O+since/for+time(Simple Sentence)
S+had+been+not+1Ving+O+since/for+time (Negative)
Had+S+not+been+1Ving+O+since/for+time (Interro-negative)
| Had | Sajid | not | go-ing | school | since | Wednesday? |
Had Sajid not been going school since Wednesday?
| Had | we | not | do-ing | hard work | since | morning? |
Had we not been doing hard work since morning?
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe an action that will have been happening for a certain period of time at a specific point in the future. It emphasizes the duration of the action up to that future moment.
Future =the period of time will be occurring/happening
Perfect = complete
Continuous =going on
Tense = time/verb
Future Perfect Continuous Tense = any complete action will be in process now
S + will have been + verb (-ing) + o
They will have been doing duty.
Examples of Future Perfect Continuous Tense for Affirmative Sentences
will have been =He, She, You, It, They, or name(s)
shall have been =I, We
| No. | Affirmative Sentence (Future Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She will have been studying for her exams all morning. |
| 2 | They will have been playing football in the park. |
| 3 | He will have been working on his project for three hours. |
| 4 | I shall have been learning Spanish for a few months. |
| 5 | The baby will have been crying for a long time. |
| 6 | We shall have been waiting for the bus for twenty minutes. |
| 7 | The teacher will have been explaining the lesson patiently. |
| 8 | John will have been fixing his car for two days. |
| 9 | The chef will have been cooking delicious meals. |
| 10 | The kids will have been watching cartoons all evening. |
| 11 | She will have been practicing the piano for hours. |
| 12 | The workers will have been repairing the road all day. |
| 13 | My mother will have been knitting a sweater for me. |
| 14 | The students will have been discussing the topic in groups. |
| 15 | The dog will have been barking at strangers. |
| 16 | He will have been jogging in the park every morning. |
| 17 | I shall have been decorating my house for the festival. |
| 18 | The gardener will have been watering the plants regularly. |
| 19 | They will have been traveling across different countries. |
| 20 | The author will have been writing a new novel for months. |
They will have been doing duty.
Negative Sentence of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after will/shall. Let us formulate it.
S+will/shall +not+have+been+4V+O
We shall not have been going school.
Here is a table with 20 important negative sentences in the Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
| No. | Negative Sentence (Future Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | She will not have been studying for the test. |
| 2 | They will not have been working on the project. |
| 3 | He will not been exercising regularly. |
| 4 | I shall not have been reading that book lately. |
| 5 | We shall not have been waiting for too long. |
| 6 | The baby will not been crying this morning. |
| 7 | You will not have been following the instructions. |
| 8 | The teacher will not have been explaining the topic well. |
| 9 | She will not have been practicing the piano. |
| 10 | He will not have been attending his online classes. |
| 11 | They will not have been traveling much this year. |
| 12 | I shall not have been feeling well for a while. |
| 13 | The dog will not have been barking at night. |
| 14 | She will not have been cooking dinner lately. |
| 15 | We shall not have been discussing the new plan. |
| 16 | He will not have been calling his friends often. |
| 17 | The company will not have been hiring new employees. |
| 18 | You will not have been preparing for the meeting. |
| 19 | I shall not have been sleeping well these days. |
| 20 | They will not have been cleaning the house properly. |
Interrogative Sentences of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interrogative, place “will” or “shall” right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Will/shall + S +been +1V+ing + O + ?
| No. | Interrogative Sentence (Future Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Will you have been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Will she have been working on her project all day? |
| 3 | Will they been playing football in the park? |
| 4 | Will he have been practicing the guitar recently? |
| 5 | Shall we have been waiting here for too long? |
| 6 | Will it have been raining heavily? |
| 7 | Will you have been feeling well lately? |
| 8 | Will the dog have been barking all night? |
| 9 | Will the kids have been watching TV for hours? |
| 10 | Will the baby have been crying a lot? |
| 11 | Will you have been learning Spanish? |
| 12 | Will she have been cooking dinner? |
| 13 | Will they have been discussing the issue seriously? |
| 14 | Will he have been reading that book? |
| 15 | Will you have been exercising daily? |
| 16 | Will the workers have been fixing the road? |
| 17 | Will the teacher have been explaining the topic clearly? |
| 18 | Shall we have been talking too loudly? |
| 19 | Will they have been planning their trip? |
| 20 | Will she have been designing new clothes? |
Interro-Negative Sentences of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “will” or “ shall“ right before the subject of a negative sentence and put a sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
(General Sentence)(Step 1)
S+will/shall+been+1V+ing+O
(Negative Sentence)(Step 2)
S+will/shall+not+have+been+1V+ing+O
(General Sentence)(Step 3)
Will/shall+S+not+have+been+1V+O?
Here is a table with 20 examples of interro-negative sentences in the Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
| No. | Interro-Negative Sentence (Future Perfect Continuous) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Will you not have been studying for the exam? |
| 2 | Will they not have been playing football since morning? |
| 3 | Shall we not have been waiting for the bus? |
| 4 | Will you not have been learning English recently? |
| 5 | Will the children not have been making noise? |
| 6 | Will the workers not have been repairing the road? |
| 7 | Will she not have been reading that novel? |
| 8 | Will he not have been working on his project? |
| 9 | Will you not have been exercising daily? |
| 10 | Will they not have been travelling around the country? |
| 11 | Will the teacher not have been explaining the topic? |
| 12 | Shall we not have been discussing this matter? |
| 13 | Will you not been watching the news? |
| 14 | Will your brother not have been attending classes? |
| 15 | Will the students not have been preparing for the test? |
| 16 | Will the birds not have been chirping all day? |
| 17 | Will the baby not have been crying for hours? |
| 18 | Will she not have been cooking dinner for the family? |
| 19 | Will they not have been waiting outside? |
| 20 | Will you not have been writing your assignment? |
Structure of Future Perfect Continuous Tense with (Time Frame)
S+will/shall+have+been+1V+ ing + O + since/for + time
Since= when time is from starting from one point of time
For= time period
For Example:
for two years, one month, half an hour
Since morning, last Summer, night, June.
| S | will/shall have | been | 1V-ing | O | since/for | time |
| We | shall have | been | do-ing | work | for | one year |
Negative Sentence for Time Frame
To make a sentence negative, place “ not” right after will/shall. Let us formulate it.
S+will/shall+not+have+been+not+4V+O+since/for+…..
- We shall not have been playing cricket for four years.
- They will not have been playing cricket for four years.
- Sajid will not have been going school since Wednesday.
Interrogative Sentence for Time Frame
To make a sentence interrogative, place“will/shall“ right before the subject or at the start of the sentence. Let us formulate it.
Has/Have+S+been+4V+O+since/for+…… ?
- Will he have been reading a book since morning?
- Shall we have been doing work for one year?
- Will Ali have been doing a job for two years?
Interro-Negative Sentences for Time Frame
To make a sentence interro-negative, add “will/shall“ right before the subject of a negative sentence and put sign of interrogation at the end. Let us formulate it.
S+will/shall+have+been+not+1Ving+O+since/for+time(Simple Sentence)
S+will/shall+not+have+been+1Ving+O+since/for+time (Negative)
Will/shall+S+not+have+been+not+1Ving+O+since/for+time (Interro-negative)
- Will Sajid not have been going school since Wednesday?
- Shall we not have been doing hard work since morning?